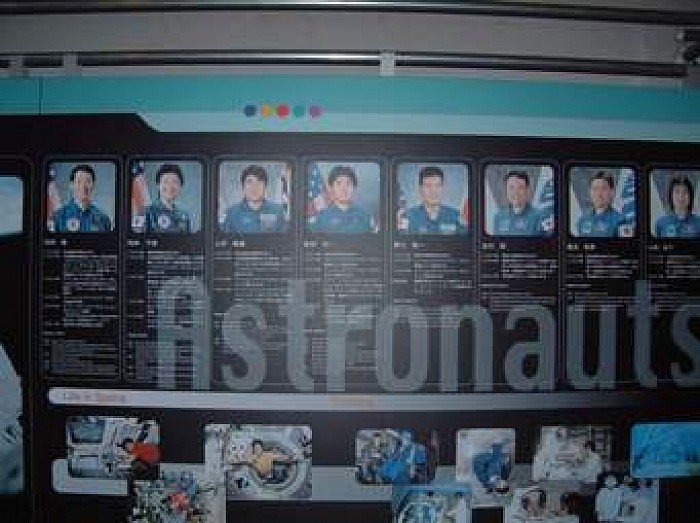
AERUTRON, JAXA/AGAWA NASA JAPAN PLANET JUPITER OBSERVATORY
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency is the Japanese national aerospace and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. Wikipedia
Budget: ¥211.11 billion/ $2.03 billion (FY2013)
Motto: One JAXA
Founded: 1 October 2003
Headquarters: Chofu, Tokyo, Japan
Jurisdiction: Japan
"ANTIHYDROGEN"
What is antimatter and its uses?
We see its signature in cosmic rays, and it is routinely made in high-energy collisions inside particle smashers the world over. In hospitals, radioactive molecules that emit antimatter particles are used for imaging in the technique known as positron emission tomography.
How is antimatter detected?
If antimatter-dominated regions of space existed, the gamma rays produced in annihilation reactions along the boundary between matter and antimatter regions would be detectable. ... The presence of the resulting antimatter is detectable by the two gamma rays produced every time positrons annihilate with nearby matter.
What does antimatter look like?
What Would An Antimatter Universe Look Like? ... The basic difference between matter and antimatter is that they have opposite charges. A proton has a positive charge, while an antiproton a negative one. Positively charged positrons are theantimatter version of negatively charged electrons.
Can you see antimatter?
We can't see antimatter but it really does matter. ... Particles of matter and antimatter are identical, except for an opposite electrical charge. An electron has a negative charge whereas its antiparticle, the positron, has a positive charge, and both have an identical mass.
Antihydrogen
Antihydrogen ( H. ) is the antimatter counterpart of hydrogen. Whereas the common hydrogen atom is composed of an electron and proton, the antihydrogen atom is made up of a positron and antiproton.
How much does antihydrogen cost?
Cost. Scientists claim that antimatter is the costliest material to make. In 2006, Gerald Smith estimated $250 million could produce 10 milligrams of positrons (equivalent to $25 billion per gram); in 1999, NASA gave a figure of $62.5 trillionper gram of antihydrogen.
Has antimatter been created?
However, humans have produced only a minuscule amount of antimatter. All of the antiprotons created at Fermilab's Tevatron particle accelerator add up to only 15 nanograms. Those made at CERN amount to about 1 nanogram. At DESY in Germany, approximately 2 nanograms of positrons have been produced to date.
Can we detect dark matter?
Dark matter is called dark because it does not appear to interact with observable electromagnetic radiation, such as light, and is thus invisible to the entire electromagnetic spectrum, making it extremely difficult to detect using usual astronomical equipment.
What can dark matter do?
Dark matter is called dark because it does not appear to interact with observable electromagnetic radiation, such as light, and is thus invisible to the entire electromagnetic spectrum, making it extremely difficult to detect using usual astronomical equipment.
Can matter be destroyed by antimatter?
If matter and antimatter are created and destroyed together, it seems the universe should contain nothing but leftover energy. Nevertheless, a tiny portion of matter – about one particle per billion – managed to survive.
Is exotic matter real?
Exotic matter. In physics, exotic matter is matter that somehow deviates from normal matter and has "exotic" properties. A broader definition of exotic matter is any kind of non-baryonic matter—that is not made of baryons, the subatomic particles (such as protons and neutrons) of which ordinary matter is composed.
Where can antimatter be found?
The discovery confirms earlier predictions that Earth's magnetic field can trap antimatter particles created by the interaction of cosmic rays with our planet's atmosphere, said study team member Alessandro Bruno, an astrophysicist at the University of Bari in Italy.
How would an antimatter engine work?
Antimatter rockets can be divided into three types of application: those that directly use the products of antimatter annihilation for propulsion, those that heat aworking fluid or an intermediate material which is then used for propulsion, and those that heat a working fluid or an intermediate material to generate...
Does antimatter exist in nature?
If antimatter-dominated regions of space existed, the gamma rays produced in annihilation reactions along the boundary between matter and antimatter regions would be detectable. Antiparticles are created everywhere in the universe where high-energy particle collisions take place.
Is there an Antineutron?
Antineutron. . It differs from the neutron only in that some of its properties have equal magnitude but opposite sign. It has the same mass as the neutron, and no net electric charge, but has opposite baryon number (+1 for neutron, −1 for the antineutron).
What is an antiproton called?
The antiproton, p. , (pronounced p-bar) is the antiparticle of the proton. Antiprotons are stable, but they are typically short-lived, since any collision with a proton will cause both particles to be annihilated in a burst of energy.
Is there antimatter in space?
If antimatter-dominated regions of space existed, the gamma rays produced in annihilation reactions along the boundary between matter and antimatter regions would be detectable. Antiparticles are created everywhere in the universe where high-energy particle collisions take place.
What is antimatter simple?
Antimatter is a term in particle physics. Antimatter is a material composed of antiparticles. These have the same mass as particles of ordinary matter but have opposite charge and properties, such as lepton and baryon number. Encounters between particles and antiparticles lead to the destruction of both.
How are antiparticles created?
Because charge is conserved, it is not possible to create an antiparticle without either destroying another particle of the same charge (as is for instance the case when antiparticles are produced naturally via beta decay or the collision of cosmic rays with Earth's atmosphere), or by the simultaneous creation of both...
Is Antimatter a solid?
Antimatter particles bind with one another to form antimatter, just as ordinary particles bind to form normal matter. For example, a positron (the antiparticle of the electron) and an antiproton (the antiparticle of the proton) can form an antihydrogen atom.
How much energy does antimatter release?
One billionth of a gram of positrons contains as much energy as 37.8 kilograms (83 pounds) of TNT, making the 2004 cost of "positron hand grenade" (10 trillionth of a gram of antimatter, 378 g TNT equivalent) that could be fitted in a sniper's bullet US$600,000.
What exactly is dark matter?
What's beyond the observable universe?
How is antimatter created naturally?
Is it true that energy Cannot be created or destroyed?
AERUTRON E=MC2
NEGATIVE
OCEANIC CRUST = e- + e+
CONTINENTAL CRUST = e- + e+
= Earth Matter / Antimatter Energy?
POSITIVE
OUTER CORE = p+ + p-
INNER CORE = p+ + p-
MASS:
Planet Earth heavy Weight of Energy by Inner Core + Outer Core + Lower Mantle + upper Mantle + Asthenosphere + Lithosphere + Oceanic Crust + Continental Crust
C2:
Speed of light (Constant) Earth and Sun light Energy
Constant = Energy?
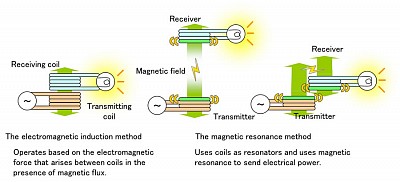
In a wireless power transmission system, atransmitter device, driven by electric power from a power source, generates a time-varying electromagnetic field, which transmits power across space to a receiver device, which extracts powerfrom the field and supplies it to an electrical load.